Animal:Z9surbj6cs8= Cell
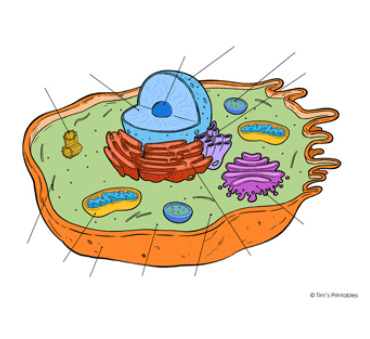
The study of animal cells serves as a cornerstone in understanding the complexities of multicellular life. Their unique properties, particularly the absence of a rigid cell wall and the presence of specialized organelles, allow for a remarkable range of functions that are critical for both organismal health and scientific advancement. As research continues to uncover the multifaceted roles of these cells, particularly in medical and biotechnological contexts, one must consider how these insights could shape future innovations in treatment and therapy. What implications could these developments hold for the future of science and medicine?
Overview of Animal:Z9surbj6cs8= Cell
Animal cells, characterized by their complex structures and specialized functions, serve as the fundamental building blocks of multicellular organisms, enabling a diverse range of physiological processes essential for life.
The intricate cell structure, comprising organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum, facilitates critical metabolic functions.
These processes, including energy production and biosynthesis, are vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis and supporting overall organismal health.
See also: Among Us:Xanc9oskqog= Sus
Unique Properties and Characteristics
One notable characteristic of animal cells is their lack of a rigid cell wall, which allows for greater flexibility and a variety of shapes.
This flexibility enables them to perform specialized functions within tissues and organs.
This unique cell structure facilitates diverse roles, including nutrient absorption and signal transduction, underscoring the intricate relationship between form and function inherent in animal cell biology.
Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology
The versatile nature of animal cells has led to their critical application in medicine and biotechnology, where they serve as foundational components in cell culture systems, drug development, and regenerative therapies.
Their ability to mimic physiological processes enables significant therapeutic applications, particularly in regenerative medicine, where they contribute to tissue engineering, stem cell therapy, and the creation of biologically compatible products for clinical use.
Future Research Directions and Implications
As advancements in genetic engineering and synthetic biology continue to evolve, future research on animal cells is poised to unlock novel therapeutic strategies and enhance our understanding of complex biological systems.
However, ethical considerations surrounding genetic manipulation and potential challenges related to regulatory frameworks must be addressed.
Balancing innovation with responsible practices will be crucial for sustainable progress in this rapidly advancing field.
Conclusion
In summary, animal cells serve as the cornerstone of multicellular life, showcasing unique properties that enable diverse functions and complex tissue structures.
Remarkably, the human body contains approximately 37.2 trillion cells, each contributing to vital biological processes.
Their applications in medicine and biotechnology underscore their significance in advancing therapeutic strategies and drug development.
Continued research into animal cell biology promises to unlock further potential, driving innovations that could transform healthcare and enhance regenerative therapies.
