Skin:Hnxv_1hcbna= Impetigo
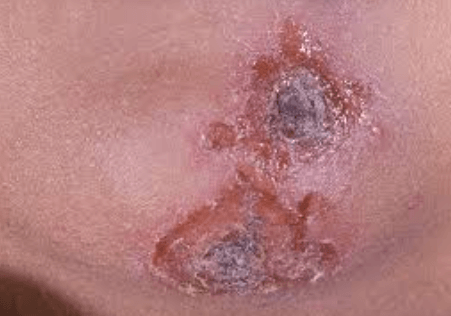
Impetigo, a highly contagious skin infection primarily caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, presents significant challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. Characterized by the emergence of red sores that ooze and crust, this infection often thrives in environments conducive to rapid transmission, especially among children. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring available treatment options are pivotal in managing this condition effectively. However, the implications of impetigo extend beyond immediate treatment, raising important questions about prevention and long-term outcomes that merit further discussion.
Causes of Impetigo
Impetigo is primarily caused by bacterial infections, most commonly attributed to Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, which infiltrate the skin through breaks or abrasions.
These pathogens thrive in moist environments, making certain skin conditions, such as eczema or insect bites, predispose individuals to infection.
The bacteria can spread rapidly, particularly among children, leading to localized outbreaks in communal settings.
See also: Snowman:95fetoerzb8= Frosty
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of impetigo is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment, as the infection typically manifests with characteristic lesions on the skin.
Patients often experience skin irritation, presenting as red sores that may ooze and crust over.
Due to its contagious nature, prompt identification is essential to prevent spread, particularly in communal settings such as schools and daycare facilities.
Treatment Options Available
Effective treatment options for impetigo primarily include topical and systemic antibiotics, which aim to eliminate the bacterial infection and promote healing of the affected skin.
Topical antibiotics, such as mupirocin or fusidic acid, are often first-line therapies.
In more severe cases, oral medications like dicloxacillin or cephalexin may be prescribed to ensure comprehensive management of the infection and prevent complications.
Conclusion
In summary, impetigo remains a significant public health concern due to its highly contagious nature and prevalence among children.
An estimated 2% of children in the United States experience this infection annually, highlighting the need for awareness and prompt treatment.
Early identification of symptoms and appropriate interventions can effectively reduce transmission rates and promote recovery.
This emphasizes the importance of education regarding hygiene practices to prevent outbreaks in communal settings such as schools and daycare centers.
