Rash:Bits0b_Vaiu= Scabies
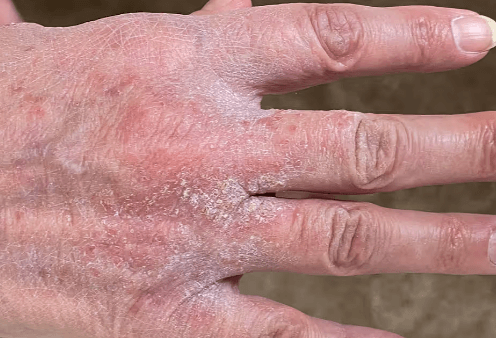
Scabies, an infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, manifests through a distinctive rash characterized by red bumps and intense nocturnal itching. This condition poses significant challenges, particularly in communal living environments, where transmission rates can escalate rapidly. Diagnosis typically relies on clinical evaluation complemented by skin scrapings, while treatment involves the application of effective topical scabicides. However, the implications of scabies extend beyond mere symptoms and treatment protocols, raising important questions about prevention and public health measures that warrant further exploration. What strategies can be implemented to mitigate outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations?
Understanding Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, leading to intense itching and a characteristic rash due to the host’s inflammatory response to the parasitic presence.
The primary causes of scabies include close physical contact and sharing personal items.
Transmission occurs through prolonged skin-to-skin contact, making it common in crowded living conditions and among individuals with compromised hygiene practices.
See also: Rare Turtles
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The hallmark symptoms of scabies include intense pruritus, often worsening at night, and the presence of a distinctive rash characterized by small red bumps, papules, and burrows, which are indicative of the mite’s activity within the skin.
This itchy rash may lead to secondary skin infections due to scratching.
Diagnosis typically involves clinical evaluation and may include skin scrapings for microscopic examination.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for scabies primarily involves the use of topical scabicides, such as permethrin cream or benzyl benzoate, which target the mites and their eggs while alleviating symptoms.
Additional medication types, including oral ivermectin, may be prescribed for severe cases.
Home remedies, while popular, lack scientific validation and should not replace conventional treatments, emphasizing the importance of professional medical guidance for effective management.
Conclusion
In the realm of skin afflictions, scabies stands as a relentless adversary, weaving its intricate web of irritation and discomfort.
The journey through its symptoms and treatment mirrors a battle against an unseen foe, where early detection and effective intervention are paramount.
Just as a vigilant gardener must tend to a flourishing garden to prevent the encroachment of weeds, so too must individuals remain proactive in addressing scabies, ensuring a return to the harmony of healthy skin.
